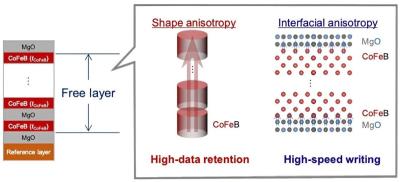
Researchers from Japan's Tohoku University developed a method to produce X nm MTJs, using a CoFeB/MgO stack structure. The researchers report that the extremely small device achieves both high-retention and high-speed. This was enabled by controlling the shape and interfacial anisotropies individually by varying the thickness of each CoFeB layer and the quantity of [CoFeB/MgO] stacks.
The researcher further report that shape anisotropy-enhanced MTJs showed good retention (> 10 years) at 150 °C at single nanometer sizes, whereas interfacial anisotropy-enhanced MTJs exhibited rapid speed switching (10 ns or less) below 1 V.
Source:
Posted: Jan 19,2024 by Ron Mertens


Comments
Thanks for the metrics
Thanks Ron for having taken the time to indicate the metrics (10 years, 150C, 10ns,…), instead of vague information : this helps to quickly benchmark the R&D results and merits, and also what improvements may still be needed compare to SRAM / DRAM.
As possible, it will also be good to indicate Read/Write endurance (10E12, 10E14, 10E16,…)