![]() Samsung is a large Korean conglomerate focusing on electronics, displays (both LCDs and OLEDs) and semiconductors. Samsung is a leading memory producer and is researching several next-generation memory technologies, including RRAM and MRAM.
Samsung is a large Korean conglomerate focusing on electronics, displays (both LCDs and OLEDs) and semiconductors. Samsung is a leading memory producer and is researching several next-generation memory technologies, including RRAM and MRAM.
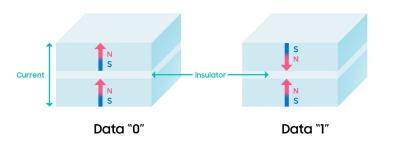
Samsung collaborates with several companies on STT-MRAM technologies, including Hynix and IBM. In April 2016 Samsung's semiconductor unit manager said that Samsung will be ready with MRAM chips soon.
In 2011 Samsung acquired Grandis, an STT-MRAM technology developer. In September 2017 it was reported that Samsung is set to start mass producing 28nm embedded MRAM. In 2021, Samsung announced it is working to scale down to 14 nm processes, and in 2024 it said it has finalized the development of its 14 nm eMRAM process, and will be ready to mass produce it by the end of 2024.
Samsung Town
Seoul
South Korea
Samsung on track to start 14 nm eMRAM production by the end of 2024, 8 nm by 2026 and 5 nm by 2027
In 2019, Samsung Electronics announced that it has started to mass produce its first embedded MRAM devices, made using the company's 28 nm FD-SOI process. In 2021, Samsung announced it is working to scale down to 14 nm processes.
The company now says that it has finalized the development of its 14 nm eMRAM process, and will be read to mass produce it by the end of 2024. The company says that the 14 nm process achieve a 33% area scaling compared to its 28 nm process, and it also enables a 2.6x faster read cycle time. Samsung says that its eMRAM enables the smallest size 16MB memory die.
Netsol Unveils First Standalone MRAM Using 28nm Process, Shares the Outlook for Standalone MRAM at 2023 MRAM Forum
At the 2023 MRAM Forum, a key event by the IEEE Magnetics Society tied to the IEDM conference, Mr. Noh, Chief Technology Officer at Netsol, provided an overview of the company's advancements in MRAM technology.
Mr. Noh introduced Netsol's development of its first standalone MRAM, created using 28nm eMRAM technology from Samsung Foundry. He presented the technical characteristics of the product, focusing on its data retention, endurance, resistance to magnetic interference and quality, which have been validated through extensive testing.
Samsung researchers update on the company's 14 nm eMRAM project
Researchers from Samsung will soon present at IEDM 2022 a new research paper that will discuss the company's latest achievements in scaling down its MRAM technology to the company's 14nm FinFET logic process.

The Samsung researchers produced a stand-alone memory with a write energy requirement of 25 pJ per bit and active power requirements of 14 mW for reading and 27 mW for writing at a 54Mbyte per second data rate. The cycling is 10^14 cycles and when scaled to a 16Mbit device, a chip would occupy 30 square millimeters.
Samsung researchers are first to demonstrate MRAM-based in-memory computing
Researchers from Samsung's Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT), have demonstrated what they say is the worldâs first in-memory computing based on MRAM, targeting next-generation AI chips.
The researchers explain that In-Memory computing is a new paradigm that seeks to perform both data storage and data computing in a memory network. In such a computing system, a large amount of data, stored in the memory network, can be executed in a highly parallel manner. Power consumption in such systems is substantially reduced.
Samsung is progressing towards 14 nm eMRAM
In March 2019 Samsung Electronics announced that it has started to mass produce its first embedded MRAM devices, made using the company's 28nm FD-SOI process. In early 2021 Samsung announced that it managed to improve the MTJ function of its MRAM, which makes it suitable for more applications, and today, at the company's 5th Annual Samsung Foundry Forum, Samsung provides more details on its MRAM roadmap.

Samsung says it is advancing its 14 nm process which will support flash-type embedded MRAM which enables increased write speed and density. Samsung targets applications such as micro controller units (MCUs), IoT and wearables for its next-gen eMRAM.
Samsung improves its MRAM performance, will expand its target applications
In March 2019 Samsung Electronics announced that it has started to mass produce its first embedded MRAM, made using the company's 28nm FD-SOI process. The company now announced that it managed to improve the MTJ function of its MRAM, which makes it suitable for more applications.

Samsung will now expand the application of its eMRAM solutions to more markets - specifically the automotive, wearable, graphic memory, low level cache, internet of things and edge artificial intelligence markets.
Mentor to provide IC test solutions for Arm's eMRAM compiler IP
Mentor announced that it will provide a unique IC test solution for the Arm's eMRAM compiler IP which is built on Samsung Foundryâs 28nm FDSOI process technology.
Mentor says it is working with Arm to leverage industry-leading Tessent software Built-In Self-Test (BIST) Design-for-Testability (DFT) technologies for testing the next-generation of Arm's eMRAM compiler IP in development.
Samsung starts shipping 28nm embedded MRAM memory
Samsung announced that it has started to mass produce its first embedded MRAM, made using the company's 28nm FD-SOI process. Samsung says that its eMRAM memory module offers higher performance and endurance when compared to eFlash, and can be integrated into existing chips.

Samsung details that its eMRAM is 1,000 times faster than its eFlash memory, and it does not require an erase cycle before writing data (unlike Flash memory). The voltage used is also lower - and in total eMRAM consumes 1/400 the energy compared to eFlash for the writing process. Samsung's MRAM capacity, though, is lower than its 3D Xpoint, DRAM and NAND flash.
Samsung to soon start mass producing 28nm embedded MRAM
Digitimes reports that Samsung Foundry will soon start mass producing MRAM chips using Samsung's 28nm fully depleted silicon-on-insulator (FD-SOI) process technology.
Digitimes says that Samsung has collaborated with NXP on this project. Samsung has completed the tape-out of its embededd MRAM which will be first applied to NXP's new low-power i.MX-series chipset targeted at automotive, multimedia and display panel applications.
Samsung reaffirms 2018 target for STT-MRAM mass production
During Samsung Electronic's Foundry Forum, the Korean chip maker reaffirmed its goal to start producing STT-MRAM chips in 2018. In fact Samsung now says that it will mass produce these chips next year, while last year it said that 2018 will only see limited production while real mass production will only begin in 2019.
Samsung announced it will produce the 2018 MRAM chips will be produced using 8-nano low power plus (8LMPP) semiconductor foundry process. Samsung sees MRAM produced by 4LPP by 2020.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page