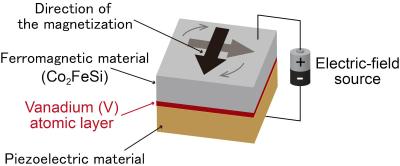
Researchers from Osaka University developed a new MRAM device architecture that enables an electric-field-based writing scheme with reduced energy consumption compared to the present current-based approach.
The researchers have developed a new component for electric field control of MRAM devices, with the key innovation being a multiferroic heterostructure with magnetization vectors that can be switched by an electric field. The researchers also demonstrate that two different magnetic states can be reliably realized at zero electric field by changing the sweeping operation of the electric field. This means a non-volatile binary state can be intentionally achieved at zero electric field.
Source:
Posted: Jan 09,2025 by Ron Mertens